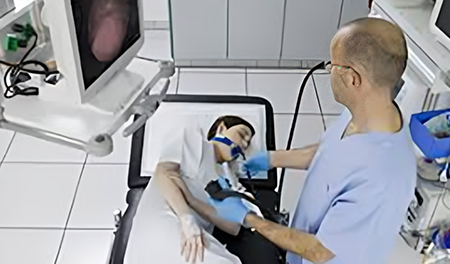
Diagnostic Endoscopy
Diagnostic endoscopy is a minimally invasive procedure that allows direct visualization of the digestive tract using a flexible tube with a camera. It helps detect, diagnose, and evaluate various gastrointestinal (GI) disorders such as ulcers, inflammation, bleeding, and early-stage cancers — ensuring precise and timely medical intervention.
Procedures
- Upper GI Endoscopy (Gastroscopy) – Examines the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum to diagnose ulcers, reflux, and bleeding.
- Colonoscopy – Evaluates the colon and rectum to identify polyps, inflammation, or colorectal cancer.
- Sigmoidoscopy – Focuses on the lower part of the colon for detecting early changes and localized issues.
- Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS) – Combines endoscopy and ultrasound for detailed imaging of the digestive organs and nearby structures.
Symptoms & Causes
Symptoms Indicating Need for Endoscopy:
- Persistent abdominal pain, nausea, or vomiting
- Unexplained weight loss or loss of appetite
- Difficulty swallowing or chronic acid reflux
- Blood in stool or vomiting of blood
Common Causes:
- Peptic ulcers or gastritis
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
- Polyps, tumors, or gastrointestinal bleeding
Benefits & Preparation
- Provides accurate, real-time diagnosis of GI conditions
- Detects ulcers, infections, or early-stage cancers before complications arise
- Helps guide treatment decisions and monitor chronic GI diseases
- Requires minimal downtime — most patients resume normal activities the same day